PROJEKTE
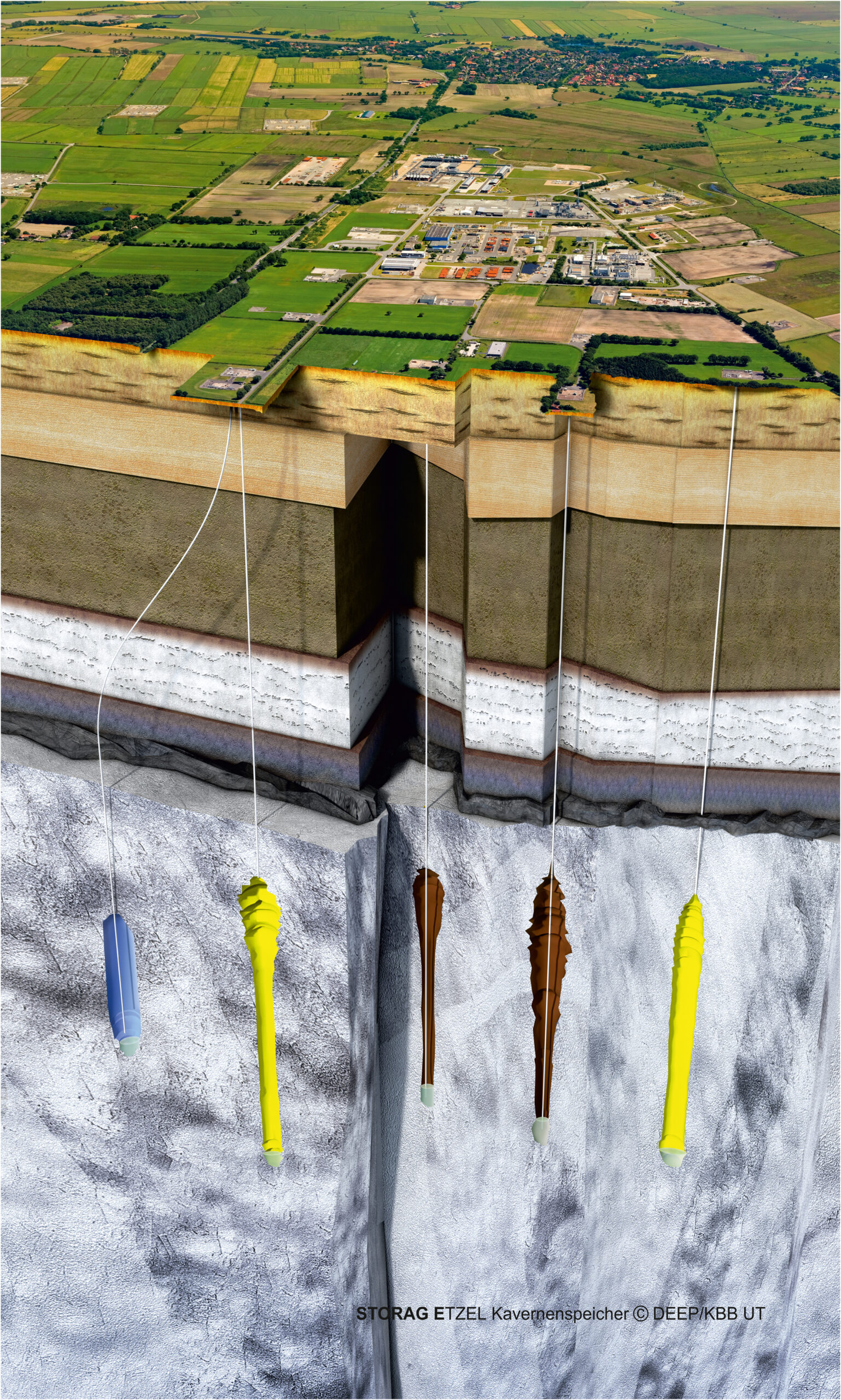
In Etzel untersuchen Experten im Verbundvorhaben H2CAST, ob die lokalen Salzstöcke zur Speicherung großer Mengen Wasserstoffs geeignet sind. ©STORAG ETZEL
SALZKAVERNEN ALS WASSERSTOFFSPEICHER
Energiespeicher spielen eine zentrale Rolle für die Versorgungssicherheit. In Niedersachsen gibt es unterirdische Salzkavernen, die bisher als Öl- und Gasspeicher genutzt wurden. Ob diese auch als Speicher für Wasserstoff fungieren können und welche Umbauten dazu gegebenenfalls notwendig sind, untersucht jetzt das Verbundprojekt H2CAST in Etzel. Das Vorhaben wird finanziell vom Niedersächsischen Ministerium für Umwelt, Energie, Bauen und Klimaschutz unterstützt.
News (05.12.2023): Zwei Kavernen für den Testbetrieb zur Wasserstoffspeicherung umgerüstet
Zwei Kavernen sind jetzt für den Testbetrieb zur Wasserstoffspeicherung umgerüstet. In den kommenden Wochen werden noch finale Tests zur Dichtigkeit durchgeführt. Sind diese erfolgreich, werden ab der zweiten Jahreshälfte 2024 bis zu 80 Tonnen Wasserstoff im Testbetrieb gespeichert. Mehr dazu hier.
News (23.10.2023): Arbeiten zur Umrüstung der Kavernen für die Wasserstoffspeicherung haben planmäßig begonnen
Die Umrüstung der zwei Kavernen hat erfogreich gestartet. „In eine Kaverne wird in die Zugangsbohrung eine Gasspeicherkomplettierung und ein Solependelstrang eingebaut. Zudem wird ein neuer für Wasserstoff geeigneter Kavernenkopf aufgebaut.“ Das Einspeisen von 80 Tonnen H2 soll im Sommer 2024 beginnen, nachdem weitere erfolgreiche Tests abgeschlossen sind. Ab 2026 soll der Standort „H2-Ready“ sein. Mehr Infos hier.
News (17.02.2023): Erfolgreicher Abschluss des ersten Dichtheitstests mit Wasserstoff an Kaverne in Etzel
Im Rahmen des Forschungsprojektes H2CAST hat STORAG ETZEL gemeinsam mit Projektpartnern den ersten Gasdichtheitstest mit Wasserstoff an einer Kavernenbohrung erfolgreich abgeschlossen.
In Vorbereitung auf den Test und während der Testphase wurden umfangreiche Materialuntersuchungen durchgeführt. Insgesamt brachte das Team mehrere tausend Normkubikmeter gasförmigen Wasserstoff aus nachhaltiger, „grüner“ Produktion in die Bohrung ein. Der Testzeitraum war mit über zwei Monaten deutlich länger, als es bei vergleichbaren Dichtheitstests unter Stickstoff der Fall ist. Mehr
News (17.01.2023): Gasunie wird Partner im Projekt H2CAST Etzel
Wie STORAG ETZEL und Gasunie am 17.01.2023 bekanntgaben, wird Gasunie Konsortialpartner im Projekt „H2CAST Etzel“. Im Rahmen des Projekts soll gemeinsam mit Projektpartnern die Wasserstoffspeicherung in den Etzeler Salzkavernen ermöglicht werden. Hierzu werden in einem ersten Schritt zwei bestehende Salzkavernen für die H2-Speicherung ertüchtigt und durch eine oberirdische Anlage verbunden. Gasunie wird für diese Obertage-Anlage verantwortlich sein. Das Pilotprojekt soll im Jahr 2026 abgeschlossen werden.
In über 750 Meter Tiefe des massiven Salzstocks Etzel lagern Gas und Erdöl in sogenannten Kavernen. Diese sind künstlich erstellte Hohlräume im Untertagebau. Das Wasserstoff-Forschung & Entwicklungsprojekt H2CAST Etzel soll aufzeigen, dass diese Kavernen nicht nur Öl und Gas, sondern auch große Mengen Wasserstoff speichern können. Die vorhandenen Kavernen sollen dann bis zu 22.5 TWh Wasserstoff vorhalten. Ein ausgeklügeltes Pendelbetriebssystem zwischen zwei Kavernen soll u.a. helfen das Speichervolumen sowie den Druck variabel anzupassen. Das Projekt im industriellen Maßstab könnte wegweisend für viele weitere Salzkavernen in Europa sein.
H2CAST ist die Abkürzung für H2 Cavern Storage Transition, und steht für die Umrüstung bestehender Kavernen und Anlagen für die Speicherung von Wasserstoff.
H2CAST Etzel Projektteam
- STORAG ETZEL (Anbieter von Kavernenspeichern)
STORAG ETZEL baut, unterhält und vermietet am Standort Etzel in Ostfriesland untertägige Speicherkapazität für Gas und Öl. Mieter sind nationale und europäische Erdölbevorratungs-Organisationen und internationale Unternehmen aus der Energiebranche. Unter anderem lagert in Etzel ein Großteil der deutschen Rohölreserve.
- Gasunie (Verantwortlich für die Obertage-Anlage)
Gasunie ist ein europäisches Energie-Infrastrukturunternehmen. Das Netz von Gasunie ist eines der größten Hochdruck-Pipelinenetze in Europa und umfasst über 17.000 Kilometer Rohrleitungen in den Niederlanden und Norddeutschland. Mit ihrer grenzüberschreitenden Gasinfrastruktur und ihren Dienstleistungen ermöglicht Gasunie den TTF, der sich zum führenden europäischen Gashandelspunkt entwickelt hat. Gasunie bietet auch andere Gasinfrastrukturdienste an, darunter Gasspeicherung und LNG.
- KBB (Planung, Bau und Betrieb von Untertagespeichern)
Die DEEP.KBB ist wesentlich mit der Planung, dem Bau und Betrieb von Untertagespeichern im Salz zur Speicherung von Erdgas, Mineralöl, Gas- und Ölprodukten sowie mit Speicherung erneuerbarer Energien, insbesondere Druckluft und Wasserstoff befasst. Schwerpunkte: Geologie, Gebirgsmechanik, Bohr- und Komplettierungstechnik, Thermodynamik, Soltechnik, Dichtheitstests, Kavernenflutungen, Gasbefüllungen und Reservoir Engineering.
- DLR – Institut für Vernetzte Energiesysteme
Das Institut für Vernetzte Energiesysteme ist im Juni 2017 ins Deutsche Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR) aufgenommen worden. Vorrangiges Forschungsziel der drei wissenschaftlichen Abteilungen Stadt- und Gebäudetechnologien, Energiesystemtechnik und Energiesystemanalyse ist die Entwicklung von Technologien und Konzepten zur Gestaltung der Energiewende.
- Hartmann Valves
Hartmann Valves ist Anbieter von Spezialkugelhähnen, Bohrlochköpfen sowie zugehörigem Service und Prüfungen, u.a. auch bei Lösungen für Anwendungen und die Untergrundspeicherung von Wasserstoff.
- TU Clausthal
Der Lehrstuhl für Geomechanik und multiphysikalische Systeme der TU Clausthal befasst sich mit der Standsicherheit und Dichtheit von Salzkavernen zur Speicherung von Energierohstoffen wie Erdgas und Erdöl, zur Druckluftspeicherung und zur Solegewinnung. Für die Wahrnehmung seiner Aufgaben in Forschung und Lehre verfügt der Lehrstuhl über ein umfangreich ausgestattetes Labor (z. Zt. 25 felsmechanische Prüfanlagen), einen leistungsfähigen Rechnerpool und diverse numerische Programmsysteme.
- SOCON
SOCON Sonar Control Kavernenvermessung ist auf die geophysikalische Vermessung von Kavernen, Bohrungen und untertägigen Hohlräumen spezialisiert.